-
1. E for Electricity (Inventor)
Introduction to electricity and electronics and how it works!
-
2. Build a Solar Car- Prototype
-
3. Solar Energy- Solar powered Car (Inventor)
Understand how to apply Solar Energy to your advantage and save the planet with the STEM Project- Solar Powered Car!
-
4. Sources of Energy- Solar Cap (Inventor)
Understand the various sources of energy that there are and learn about green and clean energy to be a Climate warrior using the STEM based Prototype- Solar Cap
-
5. Application of Wind Energy - Blow Car (Inventor)
Learn how air is different from wind and understand how to create and use wind to move objects using the STEM prototype- Blow Car!
-
6. Balloon Powered Boat - Build a Prototype (Inventor)
Understand how air pressure can influence movement of objects due to thrust
-
7. Mechanical Energy: Design a Rubber Band Powered Sail Boat (Inventor)
Discover how to make the Wind Powered Sail boat go faster using mechanical energy in the STEM Project- Sail Boat!
-
8. Sail Boat - Design Thinking (Inventor)
Understand the use of Science in your everyday and discover its importance with the help of STEM based projects and prototypes!
-
9. Design a Lantern Circuit (Inventor)
Design a STEM based prototype of an artificial light source all on your own!
-
10. In search of light (Inventor)
Know all about light and what it is made up of and learn how to use light to our advantage!
-
11. Build a Torch Light (Inventor)
Learn how to design and build your own DIY Torch Light using this STEM Project!
-
12. Design Thinking with Torch Light (Inventor)
-
13. Fun with Science - Air and its Application
- Objectives -21st Century Skills
- Materials Required
- Engage – Understanding Air and Wind
- Explore – Learn to make Bouncing bubbles
- Explore – Science of Flying
- Explore – Homemade Harmonica and Paper Pataka
- Explore – Measuring Noise Levels Around You
- Explore – Straw Whistle and six unique Ideas to Try
- Evaluate – Evaluate Your Understanding on Sound
-
14. Tinkering Toys - Design Thinking
Explore – Measuring Noise Levels Around You
Ranges of sound (Demonstration)
Materials required: A mobile smartphone
Procedure
For Android users:
- Install the Decibel Meter app on your mobile phone from the Google Play Store, linked here: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=dmytro.com.decibelmeter
- The app works with your device’s microphone.
- Open the app. It will show a certain reading of sound intensity in Decibel units (dB).
- To test the app, point the phone towards a source of the sound you want to measure (for example, you may scream in front of your phone) and observe the change in the reading (an example is shown in the pictures below).
For iOS users:
- Install the Decibel Meter app on your mobile phone from the App Store, linked here: https://apps.apple.com/in/app/sound-meter-decibel-meter/id1088469601
- If you want to understand how the app works and measures noise levels – it’s simply using your microphone.
- Open the app. It will show a certain reading of sound intensity in Decibel units (dB).
- To test the app, point the phone towards a source of the sound you want to measure (for example, you may scream in front of your phone) and observe the change in the reading (an example is shown in the pictures below).
Procedure :
- Scream “Science is awesome” and make them observe the deflection in the decibel meter app. Scream so loudly that the app reading points to at least 100.
- Now hold the phone in your hand and ask him to stand in front of the phone and say “Science is awesome”. Observe the decibel reading in the app.
- Now move a little away (a few feet distance) from the phone and say “Science is awesome”.
- Keep repeating the above step by asking the participant to move further and further away while speaking and observe the change in the decibel reading. The measurement will be updated in real-time.
How does it work?
- It is observed that the nearer the phone (that is the decibel meter app) to the sound source, the higher the reading! And the louder the sound, the higher the reading as well.
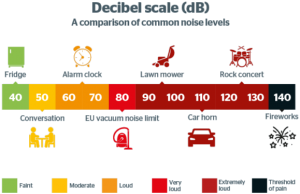
- The loudness of a sound is measured in decibels (dB). For different intensities of sound, the measured quantity shows a different reading in decibels and the sound can be divided into different types, namely loud, soft, and whisper.
- Some sounds are so loud that they are painful to our ears and others are so soft that they cannot be heard at all; some sounds are pleasant whereas some are unpleasant.
- Things that vibrate a lot make a lot of noise; they sound louder because the sound waves they generate, carry more energy.
- The loudness of a sound also depends on the distance from its source. The loudness of a sound decreases as the distance increases.
- The closer we stand in front of the sound detector app on the phone, the louder the sound and hence higher the decibel reading.
- As we move further and further away, the loudness of the sound decreases and becomes faint (because the sound has to travel over a larger distance now to reach the phone).
- If the participant keeps moving further and further away (let’s say he moved away and out of the classroom itself and finally out of the school/center building) there will be a point where his sound cannot be heard at all!
- Imagine you have to talk to two people: one standing very close to you and the other standing very far away (maybe in another room).
- Would it be easier to speak to the person next to you or the person in another room? You know the answer and it happens because sound becomes feeble (becomes faint) with increasing distance!
- Now you know why you need to raise your voice over large distances so that the other person can hear you speak.