LED which stands for Light Emitting Diode is a special type of diode that emits light when an electric current is passed through it.
How Do LED Bulbs Work?
The “light-emitting” part is self-explanatory and A diode is a semiconductor device that allows electrical current to flow easily in one direction, but severely restricts current from flowing in the opposite direction. The diode in LED is of a special type as it emits photons (light) through the principle of electroluminescence.
Don’t let that big word scare you! It essentially means that material (in this case, the diode) casts light when electrical power is applied to it.
In this Special diode (LED) Electrons jump from one side (an electron-full side) to another (an electron-deficient side) across a junction (the “p-n junction”).
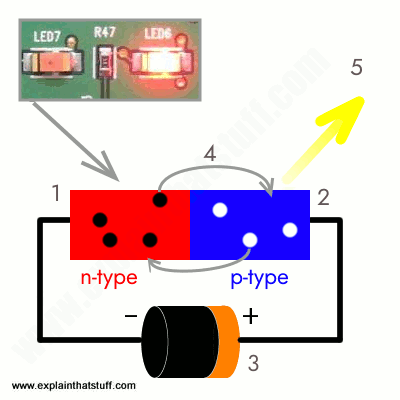

As shown in the picture above when power is applied to the p-n junction, the side lacking in electrons wants to be filled up with the charged electrons from the other side, and electrons start flowing, During this process, light is created in the light bilb.
Normal diodes are made up of either Germanium or Silicon semiconductor materials whereas Light Emitting Diodes are made from exotic semiconductor compounds such as Gallium Arsenide (GaAs), Gallium Phosphide (GaP), Gallium Arsenide Phosphide (GaAsP), Silicon Carbide (SiC), or Gallium Indium Nitride (GaInN) all mixed together at different ratios to produce different colors of light.
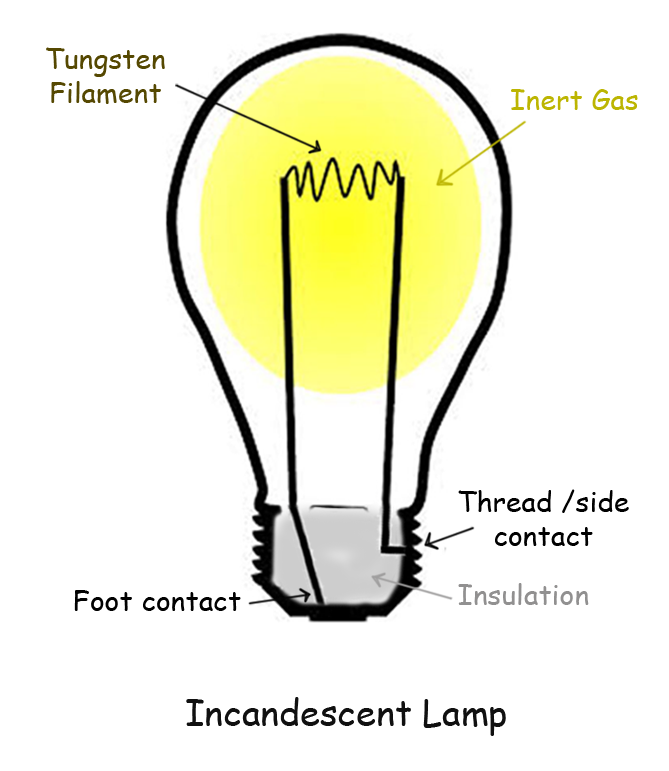
In contrast, an incandescent light bulb works by passing electricity through a small wire, or filament. The electrical resistance of the filament causes it to get so hot that it glows, producing light. The fact that LED lights do not rely on heat to wholesale usb flash drives produce its light means it runs cooler and is much more energy-efficient than an incandescent light bulb.



.
.
Learn more from MakerScientist